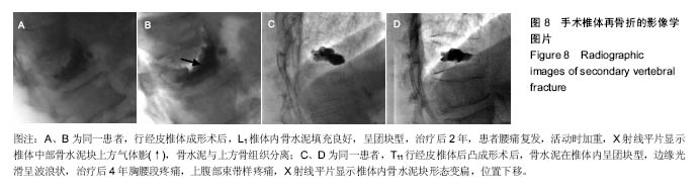
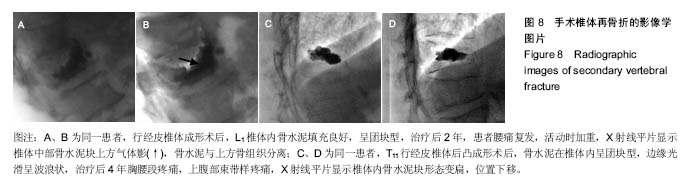
| [1]Costa F, Ortolina A, Cardia A, et al. Efficacy of treatment with percutaneous vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty for traumatic fracture of thoracolumbar junction. J Neurosurg Sci. 2009; 53(1):13-17. [2]Sun G, Jin P, Li FD, et al. Preliminary study on a single balloon cross-midline expansion via unipedicular approach in kyphoplasty. Chin Med J (Engl). 2008;121(18):1811-1814.[3]孙钢,金鹏,刘训伟,等.球囊扩张椎体后凸成形术的技术操作及相关问题的探讨[J].中华放射学杂志,2007,41(11):1224-1227. [4]吴春根,程永德.加强脊柱介入放射学的技术研究和临床应用[J].介入放射学杂志,2008,17(2):77-79.[5]全仁夫,倪月明,郑宣,等.椎体成形术骨水泥与松质骨的近期与远期改变的实验研究[J]. 中华骨科杂志,2013,33(11):1155-1163.[6]Nagad P, Rawall S, Kundnani V, et al. Postvertebroplasty instability. J Neurosurg Spine. 2012;16(4):387-393.[7]Cho SM, Heo DH, Cho YJ. Spontaneous migration of a polymethylmethacrylate mass after vertebroplasty in osteoporotic lumbar compression fracture with avascular osteonecrosis: a case report. Joint Bone Spine. 2011;78(1):98-99.[8]Lin CC, Chen IH, Yu TC, et al. New symptomatic compression fracture after percutaneous vertebroplasty at the thoracolumbar junction. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2007;28(6): 1042-1045. [9]Lee DG, Park CK, Park CJ,et al. Analysis of Risk Factors Causing New Symptomatic Vertebral Compression Fractures After Percutaneous Vertebroplasty for Painful Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures: A 4-year Follow-up.J Spinal Disord Tech. 2015;28(10):E578-583.[10]尚喜福,汤亭亭,戴尅戎.TCP-PMMA骨水泥-骨界面强度变化的研究[J].医用生物力学,2006,21(2):111-114.[11]Cherng A, Takagi S, Chow LC. Effects of hydroxypropyl methylcellulose and other gelling agents on the handling properties of calcium phosphate cement. J Biomed Mater Res. 1997;35(3):273-277.[12]Chen L,Xiang H,Li XX,et al. Improvement of Anti-Washout Performance of Calcium Phosphate Cement Using Modified Starch. Key Engineering Materials. 2007; 336-338:1628-1631.[13]Qian G, Dong Y, Yang W, et al. Injectable calcium phosphate cement and fibrin sealant recombined human bone morphogenetic protein-2 composite in vertebroplasty: an animal study. Bosn J Basic Med Sci. 2012;12(4):231-235.[14]Schumacher M, Henß A, Rohnke M,et al.A novel and easy-to-prepare strontium(II) modified calcium phosphate bone cement with enhanced mechanical properties. Acta Biomater. 2013;9(7):7536-7544.[15]Christel T, Kuhlmann M, Vorndran E, et al. Dual setting α-tricalcium phosphate cements.J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2013;24(3):573-581.[16]Tarsuslugil SM, O'Hara RM, Dunne NJ, et al. Development of calcium phosphate cement for the augmentation of traumatically fractured porcine specimens using vertebroplasty. J Biomech. 2013;46(4):711-715.[17]魏建新,纪向辉,曹飞,等.过伸复位联合单侧入路的椎体成形术治疗骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折[J].介入放射学杂志,2012,21(4): 330-333.[18]Sun G, Cong Y, Xie Z, et al. Percutaneous vertebroplasty using instruments and drugs made in China for vertebral metastases. Chin Med J (Engl). 2003;116(8):1207-1212.[19]孙钢,金鹏,刘训伟,等.经椎弓根单球囊跨中线扩张椎体后凸成形术的临床初步探讨[J].中华放射学杂志,2008,42(5): 519-522.[20]Kim YJ, Lee JW, Kim KJ, et al. Percutaneous vertebroplasty for intravertebral cleft: analysis of therapeutic effects and outcome predictors. Skeletal Radiol. 2010;39(8):757-766.[21]Huskisson EC. Measurement of pain. Lancet. 1974;2(7889): 1127-1131.[22]Fairbank JC, Couper J, Davies JB, et al. The Oswestry low back pain disability questionnaire. Physiotherapy. 1980;66(8):271-273.[23]刘训伟,魏岱旭,彭湘涛,等.经皮椎体后凸成形术在治疗骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折中恢复椎体高度局限性的观察及机制探讨[J].医学影像学杂志,2013,23(9):1457-1460.[24]Gaitanis IN, Carandang G, Phillips FM, et al. Restoring geometric and loading alignment of the thoracic spine with a vertebral compression fracture: effects of balloon (bone tamp) inflation and spinal extension. Spine J. 2005;5(1):45-54.[25]Kim MJ, Lindsey DP, Hannibal M,et al. Vertebroplasty versus kyphoplasty: biomechanical behavior under repetitive loading conditions. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006;31(18):2079-2084.[26]Graham J, Ries M, Pruitt L. Effect of bone porosity on the mechanical integrity of the bone-cement interface. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2003;85-A(10):1901-1908.[27]杨迪诚,钟建,刘涛,等.透钙磷石骨水泥制备及其载药性能[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(3):427-433.[28]Liu X, Wei D, Zhong J, et al. Electrospun Nanofibrous P(DLLA-CL) Balloons as Calcium Phosphate Cement Filled Containers for Bone Repair: in Vitro and in Vivo Studies.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2015;7(33):18540-18552.[29]刘训伟,钟建,彭湘涛,等.联合钙盐骨水泥及可降解网状微孔球囊椎体成形的体外实验[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(12):1817-1823. |